C A S E O F T H E M O N T H
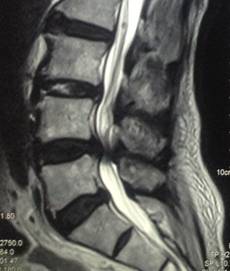 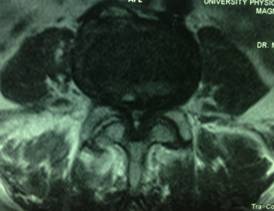
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
A 68 year old lady presented with a two year history of pain and numbness in both legs after walking for a certain distance. When this occurred, she would sit and rest until the pain and numbness went away. She also complained of low back pain but this did not bother her as much as the leg pain. At first she thought it was arthritis so she took pain relievers. Her symptoms became worse in the past few months, until she could only walk for one block before her legs became painful and numb.
On consultation with the doctor, the patient was noted to be slightly overweight. She had no weakness in her legs, and no numbness during the physical exam. The numbness would occur only after walking. She had no problems with her bladder and bowel function.
MRI of the spine showed stenosis or narrowing at the lumbar spine. The narrowing was due to thickened bone and ligaments surrounding the spinal canal, something that may happen as we grow older. Because of the narrow spinal canal, the nerves supplying the legs become compressed, especially when the patient is standing and walking. The compression becomes less when the patient is sitting or leaning forward. This is why the patient’s symptoms are worse when she is walking.
The patient underwent laminectomy and posterior decompression. This is a surgical operation wherein the bone at the back of the spinal canal is removed, in order to relieve the pressure on the nerves. To optimize her recovery, she underwent physiotherapy a couple of weeks after surgery and was given instructions on how to care for her back. She was also advised to lose weight since being overweight may contribute to the pain. The patient was able to walk for greater distances after the surgery, and the pain was much less. |